CLAT Result 2026 – The Consortium of NLUs declared CLAT 2026 results on December 16, 2025. The results were declared online at consortiumofnlus.ac.in. CLAT 2026 exam was conducted on December 7, 2025.
The direct link to download the CLAT 2026 scorecard is given below.
Log-in to the result portal using your 1) CLAT Application Number / Admit Card Number, and 2) Date of Birth.
CLAT exam result include details like total marks, All-India, and category ranks. Candidates who qualify in the exam will be shortlisted for CLAT 2025 counseling based on their scores.
The candidate was allowed to submit grievances against the conduct of the CLAT 2026 exam from December 17-24, 2025.
In the previous edition, revised results for CLAT 2025 (UG) were declared on May 17, 2025 (original results were declared on December 7, 2024). The revised results were released following a Supreme Court order after errors were found in the CLAT 2025 question paper.
Latest Updates:
- CLAT Counseling 2026 – Round I Seat Allotment OUT (Download Here)
- CLAT Result 2026 – Download Scorecard Here
- To download CLAT 2026 Result Notification – Click Here
- CLAT Answer Key 2026 – Download Link
Table of Contents
CLAT Exam Result 2026 – Highlights
| Particulars | Description |
| Who declares CLAT result | The Consortium of National Law Universities (NLUs) |
| Mode in which the results can be checked | CLAT result is released online at: https://consortiumofnlus.ac.in/ Hard-copies of the result will not be sent to the candidate. |
| Credentials required to check CLAT result | The candidate will need the following details to check CLAT 2025 result: CLAT Application Number / Admit Card Number Date of Birth |
| CLAT 2026 result date | OUT |
| Details included in CLAT scorecard | The scorecard of CLAT includes the following information: Candidate’s photograph Application No. Admit card No. Candidate’s name Date of birth Marks Obtained All-India Rank Category Rank |
| Shortlisting for CLAT counseling | Candidates will be shortlisted for counseling based on the CLAT scores. Further, allotment of seats will be made considering: Candidate’s CLAT merit rank College options selected at the time of counseling choice filling Availability of seats Category of the candidate. |
CLAT 2026 Result Portal
This is what the CLAT result log-in window will look like:
How to check CLAT 2026 results
The consortium will release the results of the CLAT 2026 exam online at consortiumofnlus.ac.in. To check your result, follow these steps:
- Go to the CLAT 2026 result portal – Click Here
- You will be redirected to a log-in window
- Enter the following credentials: 1) CLAT application number/ Admit Card Number and 2) Date of Birth
- On log-in, the CLAT 2026 scorecard will be displayed on the screen
- Download and take a printout of the scorecard.
Sample CLAT Scorecard
A sample scorecard of CLAT exam is given below for the reference of the candidate.
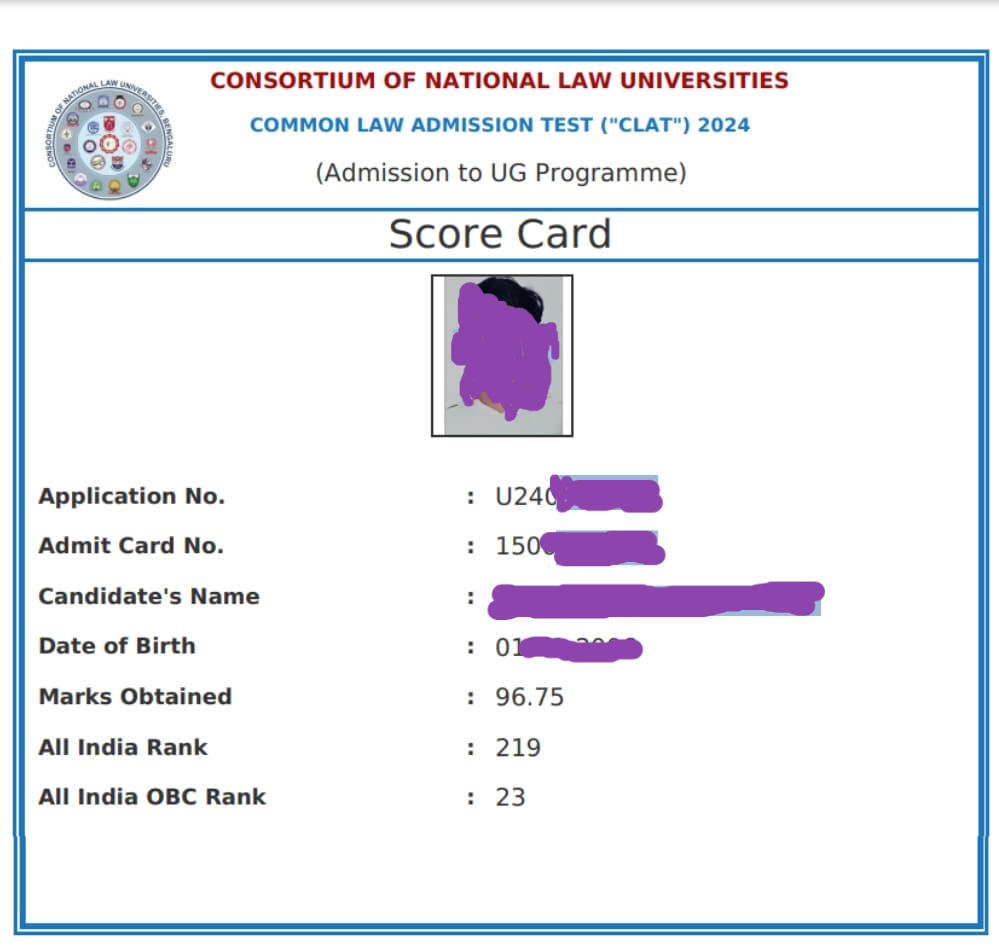
Details included in the CLAT 2026 Scorecard
The CLAT result-cum-scorecard will include the following information:
- Candidate’s photograph
- Application No.
- Admit card No.
- Candidate’s name
- Date of birth
- Marks Obtained
- All-India Rank
- Category Rank
Also Read:
- How to Prepare for CLAT
- CLAT Colleges 2026 – List of NLUs and Affiliated Law Colleges
- CLAT Question Papers
CLAT Result 2026 – Tie-breaker Policy
In case two or more candidates secure the same marks in the CLAT 2026 exam, the tie is decided based on the following rules:
| Program | CLAT 2026 Tie-breaker Policy |
| UG | The tie will be decided in the following sequence: Higher marks in the legal aptitude section of CLAT 2026 Higher age Computerized draw of lots. |
| PG | The tie will be decided in the following sequence: Higher age Computerized draw of lots |
CLAT Result 2026 – Grievance Redressa
If any candidate had any reservations against the CLAT results, they were allowed to file grievances.
The step-wise CLAT 2026 result grievance submission process is described below.
- Login to your CLAT account
- Click the ‘Submit Grievance’ button
- State the nature of your grievance;
- Describe your grievance (max. 1,000 characters);
- Upload supporting documents;
- Submit the declaration form;
- Click the Submit button
CLAT 2025 Result (UG) – Percentile Score: Number, Gender, and State-Wise Distribution of Candidates
| Percentile | Total Numbers | Gender Numbers | State Wise Numbers |
| 99.997 | 2 | Male-2 | Haryana -1 |
| Madhya Pradesh -1 | |||
| 99.995 | 1 | Male – 1 | Chattisgarh – 1 |
| 99.993 | 1 | Male – 1 | Maharashtra – 1 |
| 99.99 | 2 | Female-1 | Delhi -1 |
| Male – 1 | West Bengal- 1 | ||
| 99.988 | 1 | Male-1 | Haryana -1 |
| 99.987 | 1 | Male- 1 | Uttar Pradesh-1 |
| 99.982 | 3 | Male-3 | Karnataka-1 |
| Punjab- 1 | |||
| Uttar Pradesh-1 | |||
| 99.98 | 1 | Female- 1 | Punjab -1 |
| 99. 979 | 1 | Female- 1 | Haryana -1 |
| 99.975 | 2 | Female-1 | Maharashtra – 1 |
| Male – 1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 | ||
| 99.974 | 1 | Female – 1 | Punjab – 1 |
| 99.97 | 2 | Male- 2 | Karnataka -1 |
| Maharashtra -1 | |||
| 99.967 | 2 | Female-1 | Karnataka -1 |
| Male – 1 | Rajasthan- 1 | ||
| 99.965 | 1 | Female- 1 | Karnataka -1 |
| 99.954 | 7 | Female- 2 | Madhya Pradesh -1 |
| Male – 5 | Maharashtra – 3 | ||
| Rajasthan – 2 | |||
| West Bengal -1 | |||
| 99.936 | 11 | Female- 4 | Delhi -1 |
| Male – 7 | Jharkhand -1 | ||
| Karnataka – 3 | |||
| Kerala – 2 | |||
| Madhya Pradesh – 1 | |||
| Maharashtra -1 | |||
| Uttar Pradesh -2 | |||
| 99.919 | 10 | Female- 6 | Jharkhand -1 |
| Male – 4 | Kerala -2 | ||
| Maharashtra -1 | |||
| Rajasthan -2 | |||
| Tamil Nadu- 1 | |||
| Telangana -2 | |||
| West Bengal – 1 | |||
| 99.909 | 6 | Female- 1 | Jharkhand -2 |
| Male – 5 | Punjab – 1 | ||
| Rajasthan -1 | |||
| Uttar Pradesh – 2 | |||
| 99.904 | 3 | Female -3 | Delhi -1 |
| Rajasthan -1 | |||
| West Bengal -1 |
CLAT 2025 Result (PG) – Percentile Score: Number, Gender, and State-Wise Distribution of Candidates
| Percentile | Total Numbers | Gender wise Numbers | State wise Numbers |
| 99.993 | 1 | Female – 1 | Odisha – 1 |
| 99.986 | 1 | Female -1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 |
| 99.98 | 1 | Male -1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 |
| 99.973 | 1 | Male -1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 |
| 99.966 | 1 | Female -1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 |
| 99.959 | 1 | Male -1 | Madhya Pradesh -1 |
| 99.953 | 1 | Male -1 | Madhya Pradesh -1 |
| 99.946 | 1 | Male -1 | Madhya Pradesh -1 |
| 99.932 | 2 | Male- 2 | Bihar- 1 |
| Karnataka -1 | |||
| 99.926 | 1 | Female- -1 | Madhya Pradesh -1 |
| 99.919 | 1 | Male- 1 | Uttar Pradesh -1 |
| 99.905 | 2 | Female -1 | Uttar Pradesh -2 |
| Male- 1 | |||
| 99.892 | 2 | Male -2 | Punjab -1 |
| Uttar Pradesh -1 |
CLAT 2025 Exam Statistics – Test Centers, Attendance, Highest Marks
| Particulars | Description |
| Test Center | CLAT 2025 was conducted on Sunday, December 01, 2024, from 2 to 4 pm at: 141 Test Centers in 25 States and 4 Union Territories across India. |
| Overall attendance | 96.33% |
| Gender | Male – 57% Female – 43% 9 candidates are Transgender |
| Highest marks secured in CLAT (PG) 2025 | 80 |
| Highest marks secured in CLAT (UG) 2025 | 103.5 |
CLAT Result 2026 – Counseling Process
The Consortium of NLUs will conduct the counseling for CLAT 2026 in an online, centralized mode.
Candidates who qualify in the CLAT 2026 exam are eligible to participate in the counseling process. As part of the counseling process, the candidate will have to register and fill in choices of academic institutes in the order of priority.
As part of the counseling process, candidates are required to get registered, upload NLU preferences, and pay the counseling fee.
Also Read:









